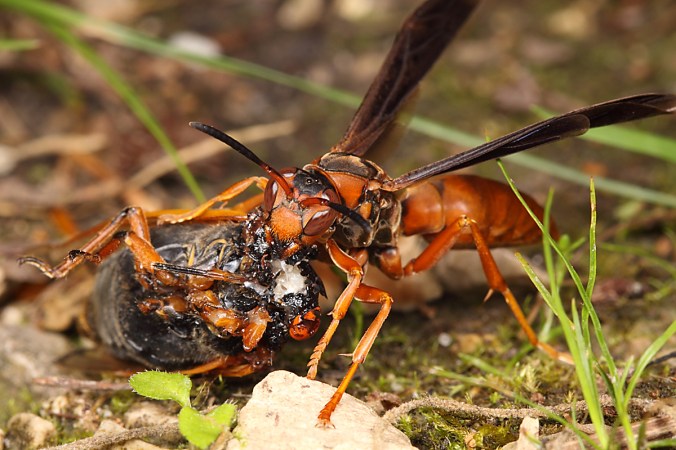
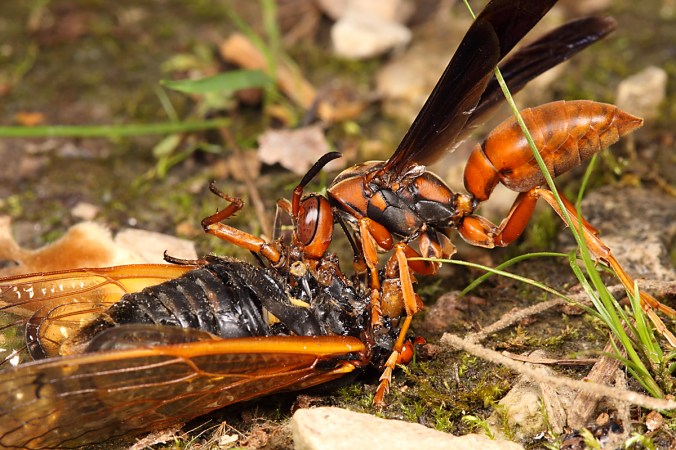
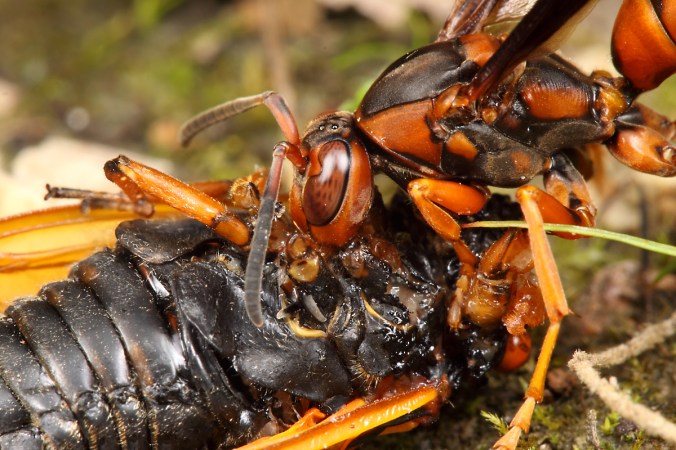
Welcome to the 7th Annual “Best of BitB”, where I pick my favorite photographs from the past year. Before I do this, however, let me briefly recap the year 2014. The trend of increasing travel each year continued, with more days spent on the road than in any prior year. Travel for work over the past few years has settled into a familiar routine—touring soybean fields in Argentina in late February and early March, working in my own field trials at (previously three, now four) sites in Illinois and Tennessee from late May through late September, touring more soybean fields at sites across the southeastern U.S. during mid-September, returning to Argentina in October to finalize plans for field trials in the upcoming season, and—finally—attending/presenting at the Entomological Society of America (ESA) Meetings (this year in Portland, Oregon). This heavy travel load makes scheduling my own insect collecting trips a bit tricky, but I’m a persistent sort! In late May I traveled to Tennessee and Georgia with fellow buprestophile Joshua Basham and lab mate Nadeer Youseff to collect several rare jewel beetles, then in late June I collected prionids and jewel beetles in Colorado, New Mexico, and Oklahoma with Jeff Huether. In addition to these longer trips, I also managed to take advantage of my work travel to check out interesting natural habitats along the way to and from my field sites. I continue to give the occasional entomology seminar as well, speaking in March at “Day of Insects” in Ames, Iowa and here in St. Louis to the Entomology Natural History Group of the Webster Groves Nature Study Society in April and the Missouri Master Naturalists Confluence Chapter in December. On top of all this, I still managed to vacation with my family in Lake Tahoe during March and in Cabo San Lucas, Mexico during late July.
I say all this to highlight the fact that after all these years I still consider myself an entomologist with a camera rather than a bona fide insect photographer. The reason for this is that the science of entomology itself remains my primary focus—photography is simply one of the tools that I have come to use in my pursuit of the discipline. I don’t mean to imply that I don’t continue to work on my photography style and technique—because I do. But my style and technique are not goals in of themselves; rather, they are means to an end—that end being my entomological studies. With that said, I present my favorite BitB photographs from 2014. As in previous years, my photos are largely hand-held, in situ field shots that are intended to tell a natural history story in a (hopefully) aesthetic manner. Links to original posts are provided for each photo selection, and I welcome any comments you may have regarding which (if any) is your favorite and why—such feedback will be helpful for me as I continue to hone my craft. If you’re interested, here are my previous years’ picks for 2008, 2009, 2010, 2011, 2012 and 2013. Once again, thank you for your readership, and I hope to see you in 2015!

Paraselenis tersa (Boheman, 1854) | Cordoba Prov., Argentina
From Tortoise beetles on the job (posted April 20). This photograph of a tortoise beetle female over her egg mass illustrates maternal guarding behavior—rare in insects. The perfect lateral profile shot and clean, blue sky background also give the photo a pleasing aesthetic quality.

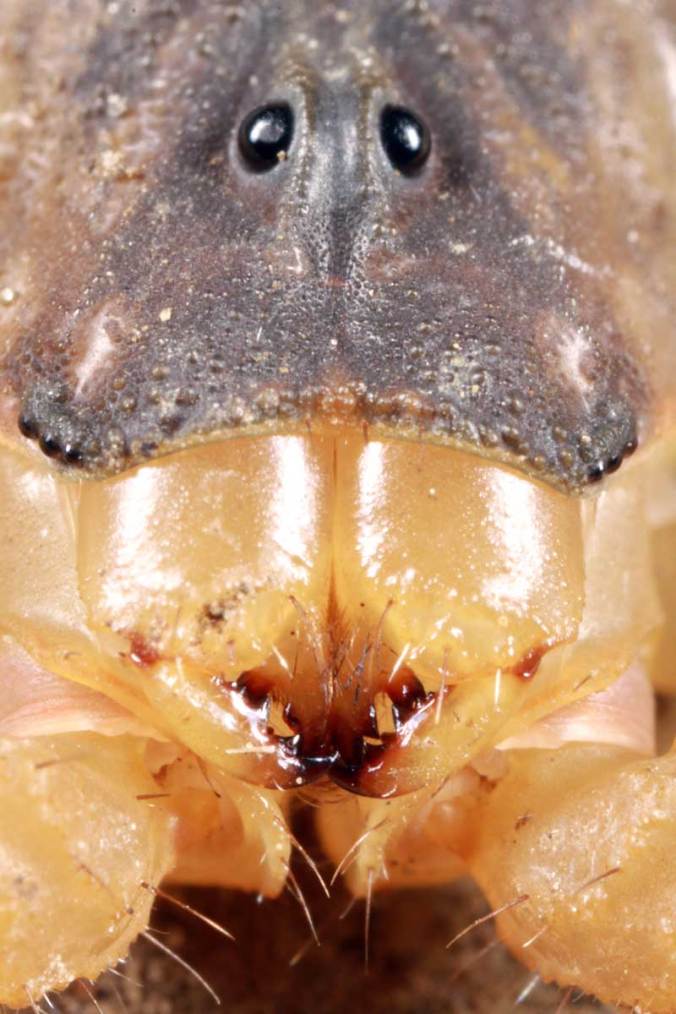
Scapteriscus borellii Giglio-Tos, 1894 | Emanuel Co., Georgia
From Who likes mole crickets? (posted June 6). This has to be the most comical expression ever on the face of an insect!

Chrysobothris orono Frost, 1920 | South Cumberland State Park, Grundy Co., Tennessee
From Chrysobothris orono in Tennessee (posted July 29). I found this rare jewel beetle for the first time this year with the help of Josh Basham and Nadeer Youseff. The beetle itself is beautiful enough, but photographing it on a pine root with a presumed adult emergence hole adds considerable natural history interest to the photo. Rock substrate behind the root adds a pleasingly blurred background.

Buprestis (Stereosa) salisburyensis Herbst, 1801 | South Cumberland State Park, Tennessee.
From The Buprestis tree (posted August 10). This was another of several jewel beetles that I found for the first time after more than three decades of collecting this group. I like the value contrast in this photo from the striking, metallic colors of the beetle against the nicely blurred cinnamon-colored pine bark of the tree on which it is sitting.

A “super moon” watches over a parasitized hornworm caterpillar.
From A time of reckoning (posted August 13). I fully admit this is a composite photograph. Nevertheless, it is a faithful recreation of a true sight, and I don’t consider the use of composite techniques to overcome equipment shortcomings to be unethical. There is a haunting symmetry between the blood red moon—considered by some as a sign of the second coming—and the sad, parasitized caterpillar waiting for its inevitable demise.

Phyllopalpus pulchellus Uhler, 1864 | Hickman Co., Kentucky
From My, what busy palps you have! (posted September 2). I’ve become quite fond of insect photos with the subject “peering” at me, the photographer”, from some unusual vantage point. The “pupils” in the eyes of this red-headed bush cricket give the insect an almost quizzical look.

Acmaeodera immaculata Horn, 1878 | vic. Vogel Canyon, Otero Co., Colorado.
From Sunset beetles (posted September 30). Taking photos of insects at sunset is a challenging and ephemeral experience—one has only a few minutes to take advantage of the unusual and serene colors it offers, while at the same time trying to determine the best camera and flash settings to use in the rapidly fading light. Of the several that I’ve tried, this one is my favorite because of the softly complimentary colors of the beetle, the flower upon which it is sitting, and the dying orange sky behind it. If I had to choose, I would probably pick this one as my favorite of the year because of the unusual and serene colors.

Megacyllene decora (Olivier, 1795) | Stoddard Co., Missouri
From Amorpha borer on goldenrod (posted October 5). I featured this very same species in Best of BitB 2012 but can’t resist choosing this second attempt at photographing the spectacularly beautiful adult—this time on goldenrod. As with the previous version this is a true in situ field photograph, hand held and using the left-hand technique to achieve precise composition against a clear blue sky—difficult to do with an insect of this size and using a 100-mm lens, but well worth the effort.

Buprestis (Knulliobuprestis) confluenta Say, 1823 | Woods Co., Oklahoma
From A Buprestis hat-trick! (posted October 14). I didn’t take near as many of the classic “frontal portraits” this year, but this one of a jewel beetle that had eluded me for more than 30 years until this past June is perhaps my favorite of them all.

Agrilus concinnus Horn, 1891 | Stoddard Co., Missouri
From North America’s Most Beautiful Agrilus Jewel Beetle (posted October 19). There was a time when this beetle was considered one of North America’s rarest species of jewel beetle. Several years worth of hunting by me and others revealed this beetle’s association with mallow and its unusually late adult activity period—the two combining to make this beetle “seem” rare. This year I succeeded in photographing the spectacular adult beetle.

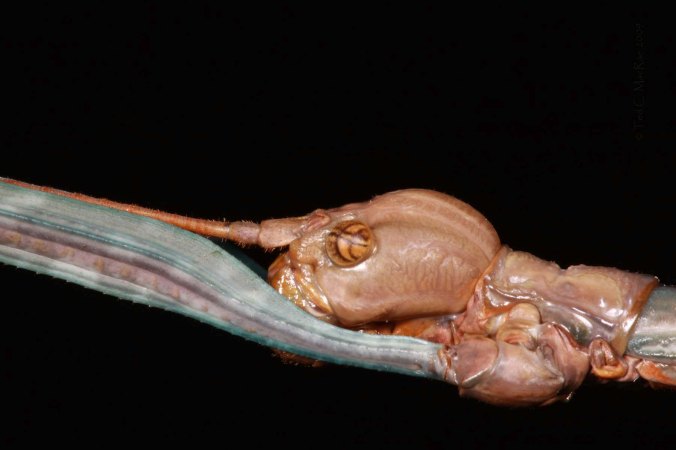
Cacama valvata (Uhler, 1888) | Vogel Canyon, Otero Co., Colorado
From Scorching plains, screaming cactus (posted December 5). Insect photos are always better when they also show some aspect of the subject’s natural history. I was lucky to find this female cactus dodger cicada in the act of ovipositing into the dry stem of cholla cactus—in a position where I could get a perfect lateral profile with a clean, blue sky background.

Moneilema armatum LeConte, 1853 | Vogel Canyon, Otero Co., Colorado
From Cactus beetle redux (posted December 20). Cactus beetles can be difficult to photograph, but sometimes they cooperate by nicely posing on a pleasing pink flower bud with a blue sky in the background and the cactus spines forming a nice, fuzzy “halo” around the jet black beetle. There were surprisingly few cactus spines impaled in the control unit of my flash after this photo session.
I hope you’ve enjoyed this 2014 version of “Best of BitB” and look forward to seeing everyone in 2015.
Copyright © Ted C. MacRae 2015