I return to my Afrikaans theme with a distinctive group of ground beetles (family Carabidae) called tyrant ground beetles or spotted ground beetles (tribe Anthiini). I think I prefer the former. This tribe is largely restricted to Africa and is especially diverse and abundant in the arid, sandy Karoo and Kalahari regions of southern Africa (Scholtz & Holm 1985). These beetles are large, powerful predators that rely on speed and agility for capturing prey, and since they are also flightless these characteristics come in handy for avoiding becoming prey themselves. Failing that, they employ chemical defense in the form of secretions from a pygidial gland located in the area of the ninth abdominal segment. The chemical cocktail within these secretions contains concentrated organic acids or quinone that can be squirted at potential predators in a strong jet. This is an effective deterrent to small mammalian and avian predators, and I suppose a careless beetle collector might also regret handling these beetles without due respect. These defensive spray capabilities give rise to another common name for the group, “oogpister” – an Afrikaner word that literally translates to (ahem) “eye pisser.”
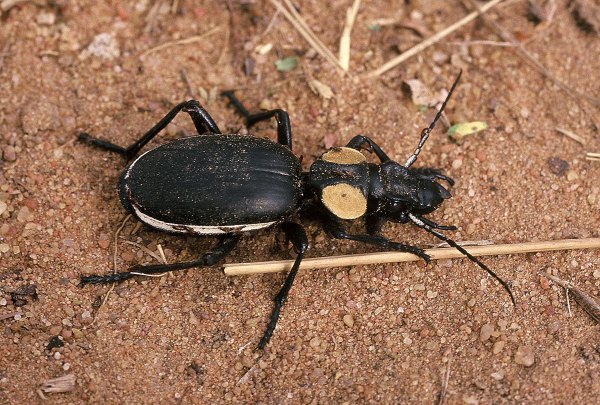 During my time in Africa, Chuck Bellamy and I were primarily focused on collecting buprestids. However, we still couldn’t resist hanging an ultraviolet light in front of a sheet and searching the ground with flashlights at night to see what diversity of other African insects we might encounter. Truth be told, one of the non-buprestid groups that I’d really hoped to encounter was a near relative of these beetles – the so-called “monster tiger beetles” of the genus Manticora (family Cicindelidae1). We never did see any monsters, but we did encounter several species of anthiine ground beetles around our encampment at Geelhoutbos farm near the Waterberg Range in Limpopo Provice. Anthia (s. str.) thoracica, the giant African ground beetle (above), was the most impressive of these. Click on the photo to see a larger version – only then will it begin to convey how truly appropriate such a common name is for this species. It is certainly the largest ground beetle that I have ever seen – a full 50 mm in length! That’s 2 inches, folks! This species is easily recognized by the depressed lateral expansions of the pronotum covered with dense white/yellow pubescence, and the slightly smaller male that I caught exhibits more elongated mandibles (though not so incredibly as in Manticora) and marvelous lobes extending backward from the pronotum.
During my time in Africa, Chuck Bellamy and I were primarily focused on collecting buprestids. However, we still couldn’t resist hanging an ultraviolet light in front of a sheet and searching the ground with flashlights at night to see what diversity of other African insects we might encounter. Truth be told, one of the non-buprestid groups that I’d really hoped to encounter was a near relative of these beetles – the so-called “monster tiger beetles” of the genus Manticora (family Cicindelidae1). We never did see any monsters, but we did encounter several species of anthiine ground beetles around our encampment at Geelhoutbos farm near the Waterberg Range in Limpopo Provice. Anthia (s. str.) thoracica, the giant African ground beetle (above), was the most impressive of these. Click on the photo to see a larger version – only then will it begin to convey how truly appropriate such a common name is for this species. It is certainly the largest ground beetle that I have ever seen – a full 50 mm in length! That’s 2 inches, folks! This species is easily recognized by the depressed lateral expansions of the pronotum covered with dense white/yellow pubescence, and the slightly smaller male that I caught exhibits more elongated mandibles (though not so incredibly as in Manticora) and marvelous lobes extending backward from the pronotum.
1 Increasingly placed within the Carabidae as subfamily Cicindelinae on the basis of molecular phylogenetic analysis, along with Paussinae and Rhysodinae (e.g., Beutel et al. 2008).
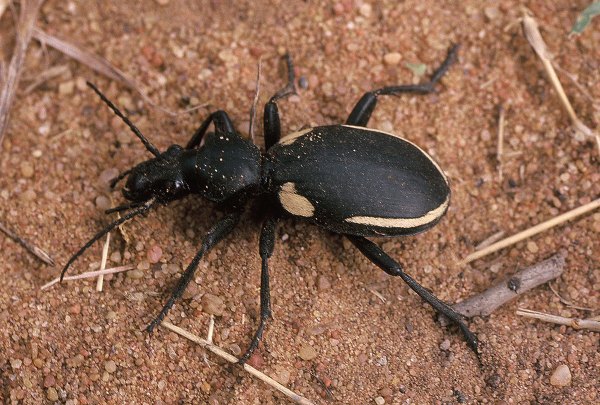 In addition to true Anthia, we saw two species of the subgenus Anthia (Termophilum)2. The species shown right is A. (T.) omoplata3, with the common name “two-spotted ground beetle” (Picker et al. 2002). It was almost as large as its giant brother above, measuring 47 mm in length. Of this species, I only saw this one individual, but I did also find two individuals of a related species, T. fornasinii. Unfortunately I was unable to photograph the latter species, which is equally large but with the elytral white markings limited to a thin marginal band and the surface of the elytra bearing strong longitudinal intervals – a handsome beast, indeed! Picker et al. (2002) mention T. homoplatum being a diurnal hunter, but we found all of our anthiines active nocturnally.
In addition to true Anthia, we saw two species of the subgenus Anthia (Termophilum)2. The species shown right is A. (T.) omoplata3, with the common name “two-spotted ground beetle” (Picker et al. 2002). It was almost as large as its giant brother above, measuring 47 mm in length. Of this species, I only saw this one individual, but I did also find two individuals of a related species, T. fornasinii. Unfortunately I was unable to photograph the latter species, which is equally large but with the elytral white markings limited to a thin marginal band and the surface of the elytra bearing strong longitudinal intervals – a handsome beast, indeed! Picker et al. (2002) mention T. homoplatum being a diurnal hunter, but we found all of our anthiines active nocturnally.
2 Treated variously in the literature as either a full genus or as a subgenus of Anthia. I follow Carabidae of the World, in which it is given subgeneric status. The name is often cited as “Thermophilum” in the literature, but this is an incorrect subsequent spelling according to Alexandre Anischenko (in litt.), coordinator/editor of Carabidae of the World.
3 Usually cited as “homoplatum” or “homoplata” in the literature, but this is an incorrect subsequent spelling (Anischenko in litt.).
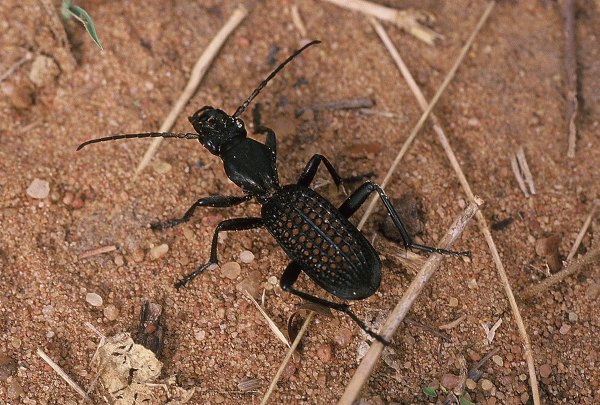 A second genus in the tribe is Cypholoba, represented here by C. alveolata. As far as I can tell it lacks a common name, which is not surprising since it is somewhat smaller than the Anthia species mentioned above. Still, my two specimens measure 38 and 35 mm in length – not puny by any standard. There can be no doubt as to the origin of the specific epithet of this species’ scientific name, with its marvelously alveolate elytra. I don’t think I’ve seen such an extraordinary example of this type of surface sculpturing on a beetle of this size, making the species every bit as spectacular as the larger anthiines.
A second genus in the tribe is Cypholoba, represented here by C. alveolata. As far as I can tell it lacks a common name, which is not surprising since it is somewhat smaller than the Anthia species mentioned above. Still, my two specimens measure 38 and 35 mm in length – not puny by any standard. There can be no doubt as to the origin of the specific epithet of this species’ scientific name, with its marvelously alveolate elytra. I don’t think I’ve seen such an extraordinary example of this type of surface sculpturing on a beetle of this size, making the species every bit as spectacular as the larger anthiines.
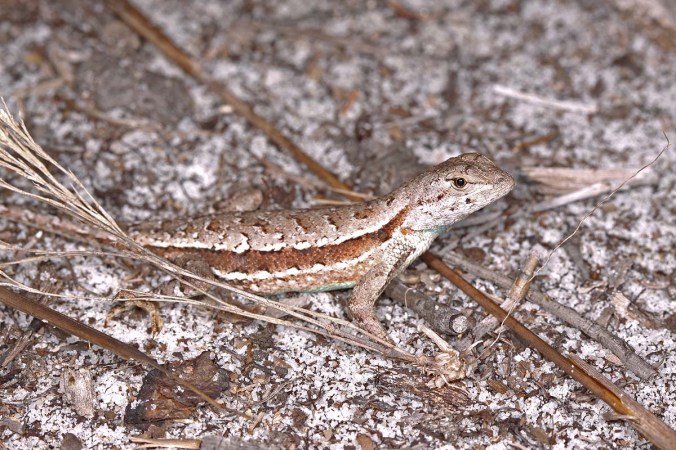
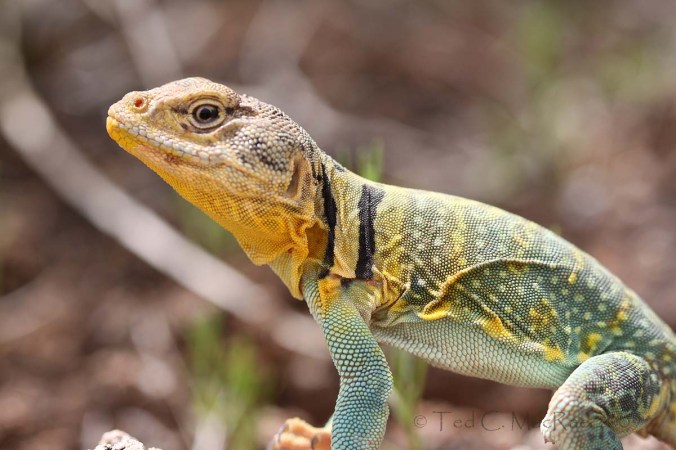
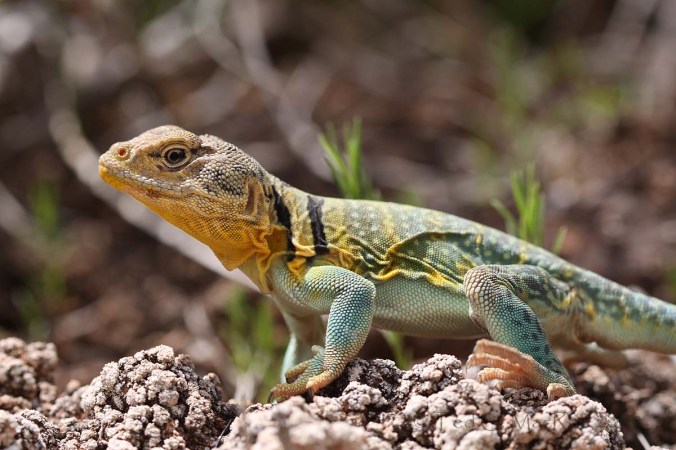
A truly fascinating aspect of Africa’s tyrant ground beetles is their role as models in Batesian mimicry systems. That these beetles should serve as models is not at all surprising due to their chemical defensive capabilities and obviously aposematic coloration. What is surprising is the mimic – juveniles of the lizard species, Eremias lugubris, in what is believed to be the first reported case of a terrestrial vertebrate mimicking an invertebrate (Huey & Pianka 1977). The juveniles not only copy (roughly) the black and white coloration of anthiine beetles but also mimic their rapid, skitty movements – foraging actively with “jerky” motions and arched backs. Their tails remain somber colored, however, allowing them to blend into the sand. These adaptations combine to give the harmless little lizard the size, color, profile, and gait of the beetles. As the lizards reach adulthood (and their greater size makes them less prone to predation), they take on a more typical cryptic coloration and move in a slower, more deliberately lizard-like manner. This mimicry association effectively reduces predation of the juveniles by potential predators, who quickly learn to avoid the noxious, and more frequently encountered, anthiine models.
REFERENCES:
Beutela, R. G., I. Riberab and O. R. P. Bininda-Emonds. 2008. A genus-level supertree of Adephaga (Coleoptera). Organisms, Diversity & Evolution, 7:255–269.
Huey, R. B. and B. R. Pianka. 1977. Natural selection for juvenile lizards mimicking noxious beetles. Science, 195 (4274):201-203.
Picker, M., C. Griffiths and A. Weaving. 2002. Field Guide to Insects of South Africa. Struik Publishers, Cape Town, 444 pp.
Scholtz, C. H. and E. Holm (eds.). 1985. Insects of Southern Africa. Butterworths, Durbin, 502 pp.