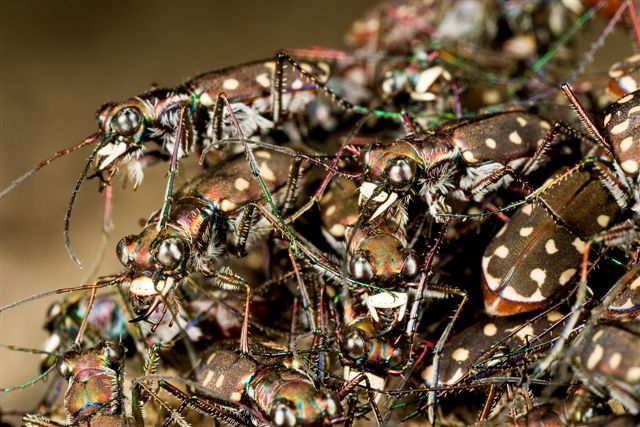
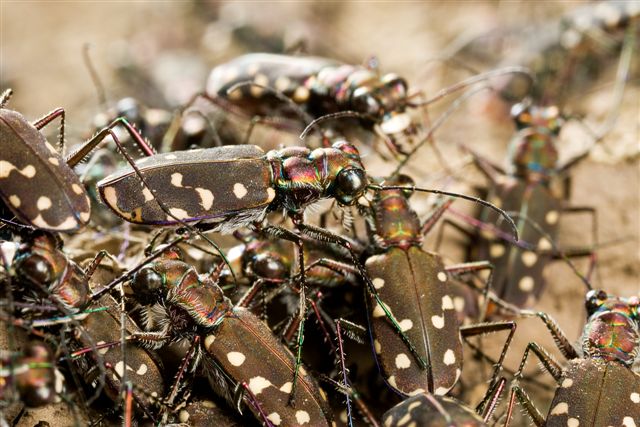
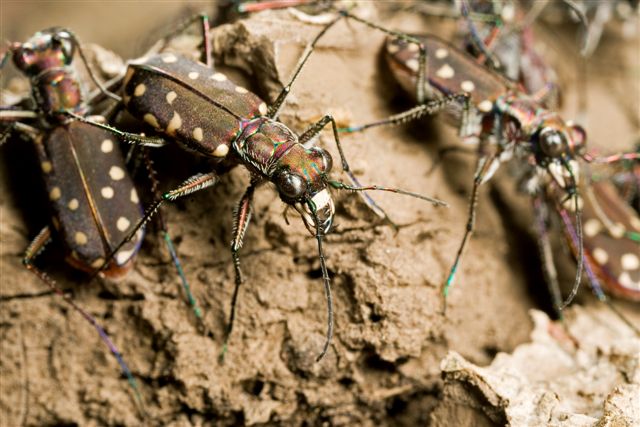
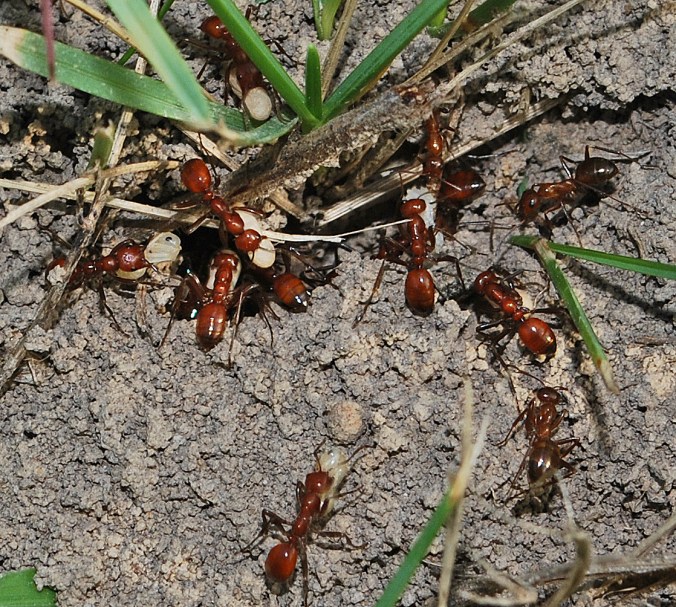
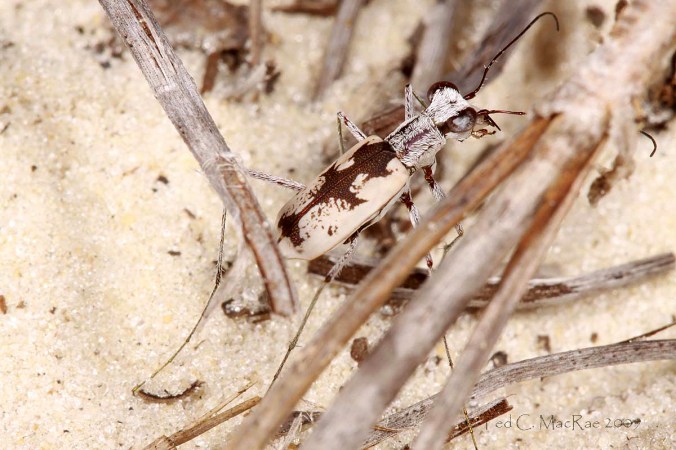
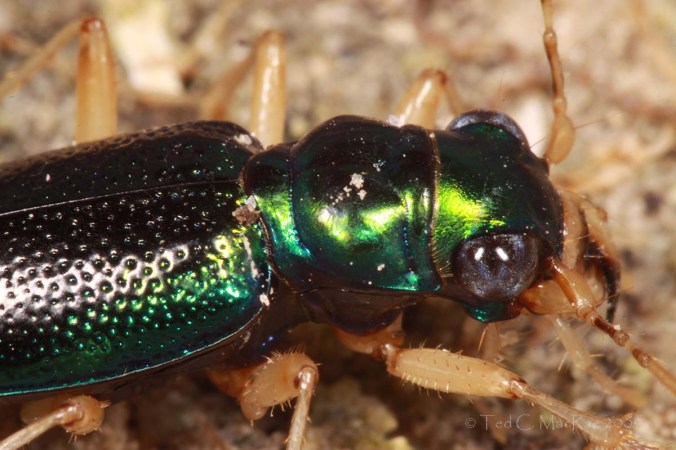
Not long ago, I received an interesting series of photographs from Joe Warfel, a nature photographer and macro specialist based in Massachussetts. Joe traveled to Arizona last July, where he photographed an aggregation of Cicindela (Cicindelidia) sedecimpuntata (Western Red-bellied Tiger Beetle¹) near a small pool in the bottom of a dry creek bed at night. Joe estimates that there may have been as many as 200 to 300 beetles per square meter in the aggregation, most of which were just “hanging out” and with only occasional individuals mating or feeding on moths that had been attracted to his headlamps.
¹ Found in the Sonoran and Chihuahuan Deserts of the southwestern U.S. and south through Mexico to Costa Rica. U.S. and northern Mexican populations are assigned to the nominate subspecies, while more southern populations are classified into four additional subspecies (Erwin and Pearson 2008).
Western Red-bellied Tiger Beetles are among the first tiger beetles to appear prior to the summer monsoons in the Sonoran Desert. The species is famous for its daytime aggregations of as many as several thousand individuals, which congregate along the drying waterways and prey upon stranded tadpoles and other aquatic organisms (Pearson et al. 2006). Joe noted that he has seen these aggregations many times before during the daytime at small pools and mudflats, with beetles usually mating and feeding frantically. However, the aggregation shown in these photographs differs from those daytime aggregations by the relative inactivity of the beetles and the fact that they were congregated on dry ground rather than the moist areas that they frequent during the daytime. In these respects, it seems to more resemble a communal nocturnal roost such as has been reported for several species of Odontocheila in South America. In those cases, up to 70 beetles have been found resting on the foliage of low shrubs, apparently as an adaptation to avoid predation by multiplying chemical defense effectiveness as well as awareness of approaching enemies (Pearson and Vogler 2001 and references therein). Cicindela sedecimpunctata is primarily a diurnal species (i.e., it is active during the daytime), though individuals are often attracted to lights at night, and adults of most diurnal species have been reported spending the night protected in burrows or under detritus and vegetation. I am not aware of communal nocturnal roosts as a reported behavior for C. sedecimpunctata or any other North American tiger beetle species.
It is a bit ironic to think of tiger beetles – voracious predators that they are – as prey, but they must have many of their own predators to deal with since most species employ multiple antipredator mechanisms. In addition to the communal roosting behavior seen in these photos, a second antipredator characteristic exhibited by this species can be seen in their bright orange abdomen. The abdomen is fully exposed only during flight, seemingly implying a “flash coloration” function for the bright color that disappears upon landing, momentarily confusing potential predators. However, Pearson (1985) experimentally determined that orange abdomens in tiger beetles actually have an aposematic function in protecting them from predation against robber flies. Most tiger beetle species with an orange abdomen also release a combination of benzaldehyde and cyanide² when captured (any tiger beetle collector is familiar with the characteristic “fruity” smell of a tiger beetle releasing benzaldehyde). Pearson painted the abdomen of paper tiger beetles models either orange or black and endowed them with or without a drop of fresh benzaldehyde. When presented on a tether to robber flies in the field, orange-abdomened models with benzaldehyde triggered significantly fewer attacks from robber flies than any other combination. Interestingly however, vertebrate predators (lizards and birds) were not deterred by the defense chemicals or by the orange abdomen, perhaps explaining why only some and not all tiger beetle species produce defense chemicals and have bright orange abdomens (Pearson and Vogler 2001).
² Tiger beetles, thus, join millipedes as being among the few invertebrates that are capable of producing cyanide.
My sincere thanks to Joe Warfel for allowing me to use his photographs. More of his work can be seen at Eighth-Eye Photography. Joe also recently had several images published in American Scientist magazine (November/December 2009 issue) for an article on harvestmen. Check out the jaws on that juvenile!
REFERENCES:
Erwin, T. L. and D. L. Pearson. 2008. A Treatise on the Western Hemisphere Caraboidea (Coleoptera). Their classification, distributions, and ways of life. Volume II (Carabidae–Nebriiformes 2–Cicindelitae). Pensoft Series Faunistica 84. Pensoft Publishers, Sofia, 400 pp.
Pearson, D. L. 1985. The function of multiple anti-predator mechanisms in adult tiger beetles (Coleoptera: Cicindelidae). Ecological Entomology 10:65–72.
Pearson, D. L., C. B. Knisley and C. J. Kazilek. 2006. A Field Guide to the Tiger Beetles of the United States and Canada. Oxford University Press, New York, 227 pp.
Pearson, D. L. and A. P. Vogler. 2001. Tiger Beetles: The Evolution, Ecology, and Diversity of the Cicindelids. Cornell University Press, Ithaca, New York, 333 pp.
Copyright © Ted C. MacRae 2010