This past June might be the most successful month entomologically that I’ve ever had. The excitement of discovering a robust population of Cylindera celeripes (swift tiger beetle) (previously considered one of North America’s rarest tiger beetles) in northwestern Oklahoma lasted only two weeks before being eclipsed by our long-awaited success at finding this same species also in Missouri. Icing on the cake was provided by finding Ellipsoptera macra (sandy stream tiger beetle) – the last tiger beetle species we had yet to encounter in Missouri, and significant new records for the tiny prairie cicada, Beameria venosa, and the impressive robber fly, Ospriocerus abdominalis, in Missouri’s critically imperiled loess hilltop prairies. With that rapid-succession-success, my thoughts immediately turned to another of Missouri’s unique natural communities – the dolomite glades of the White River Hills in the extreme southwestern part of the state. In fact, I had already been yearning to return to the White River Hills, having last visited some years ago and recalling – from the perspective now as an insect photographer – the many photogenic insect species that I’ve encountered there. Chief among them is Plinthocoelium suaveolens (bumelia borer), a spectacularly beautiful longhorned beetle of neotropical affinity that must be seen to be believed and which I had observed here several years ago in fair numbers as they perched on the lower trunks of their presumed larval host, Sideroxylon (= Bumelia) lanuginosa of the family Sapotaceae. I had even mentioned to my colleague Chris Brown, as we began the first day of our planned multi-weekend search for C. celeripes and C. macra in northwestern Missouri, that my dream scenario was that we would find both celeripes and macra on that first weekend, negating the need for additional survey the following weekends, in which case we could shoot down to the White River Hills to look for Plinthocoelium. Who knew how prescient that comment would be!

Megaphasma denticrus - giant walkingstick
I won’t keep you in suspense – I succeeded in finding and photographing Plinthocoelium, although (happily) there is more to the story than just that. I’ll share that experience here soon, but first I want to discuss another insect I saw on the first of my two July visits to the White River Hills – Megaphasma denticrus¹ (giant walkingstick). As implied by its common name, this walkingstick is enormous – females (typically larger than males) can reach lengths of 150+ mm (that’s 6 inches, folks!), making it officially the longest insect species in all of North America.  The female I feature here was solidly in that range, and with her front legs held outstretched in front of her (as pictured above), total length exceeded 8 inches. Of course, this pales in comparison to a related species from Borneo, individuals of which have been documented measuring more than 18 inches in length! The giant walkingstick is distributed primarily in the south-central U.S. – especially Texas, although records do exist from as far north and east as Iowa, Wisconsin, and Indiana (Arment 2005). I have encountered this species a few times before – always in the White River Hills, but Arment (2005) also records the species from several other counties in the Ozark Highlands across southern Missouri and Arkansas. In addition to its great size, both sexes of this species can be distinguished from other walkingsticks by the rows of numerous teeth on the underside of the middle (meso-) femur (easily seen in the enlarged view of Photo 2 above) and by the very long antennae (longer than the front femur). Color is variable – other individuals I have seen are tan with bright red dorsal stripes on the thoracic segments.
The female I feature here was solidly in that range, and with her front legs held outstretched in front of her (as pictured above), total length exceeded 8 inches. Of course, this pales in comparison to a related species from Borneo, individuals of which have been documented measuring more than 18 inches in length! The giant walkingstick is distributed primarily in the south-central U.S. – especially Texas, although records do exist from as far north and east as Iowa, Wisconsin, and Indiana (Arment 2005). I have encountered this species a few times before – always in the White River Hills, but Arment (2005) also records the species from several other counties in the Ozark Highlands across southern Missouri and Arkansas. In addition to its great size, both sexes of this species can be distinguished from other walkingsticks by the rows of numerous teeth on the underside of the middle (meso-) femur (easily seen in the enlarged view of Photo 2 above) and by the very long antennae (longer than the front femur). Color is variable – other individuals I have seen are tan with bright red dorsal stripes on the thoracic segments.
¹ Formerly classified with grasshoppers and their kin in the order Orthoptera, walkingsticks are now placed their own order, Phasmatodea, the name being derived from the Greek phasma (apparition, ghost) in reference to their cryptic appearance and behavior (the alternative spellings Phasmodea and Phasmida are improper formations from the Greek root – see Grimaldi and Engel 2005). The genus name, Megaphasma, thus means “giant walkingstick.” The specific epithet, denticrus, is derived from the Latin den (tooth) and crus (leg), presumably a reference to the toothed underside of the mesofemur. Many authors, including even some taxonomists (e.g., Beamer 1932), have mispelled the name as “dentricus” – nonsensical in Latin – with some even using both spellings in the same paper (e.g., Maginnis et al. 2008)!
Of course, an outstanding feature of this species, and all walkingsticks in general, is its uncanny resemblance to sticks and twigs. This cryptic appearance is further augmented behaviorally by the habit of “swaying” back and forth to simulate movement in a gentle breeze. I must confess that I did not even notice this large female individual – less than two feet away on a low branch – until she started moving about. Once spotted, a walkingstick of this size would seem to be a tasty – and defenseless – morsel for some avian predator; however, they have another defensive tactic up their sleeve – autotomy (i.e., the ability to shed appendages in response to predatory attack). 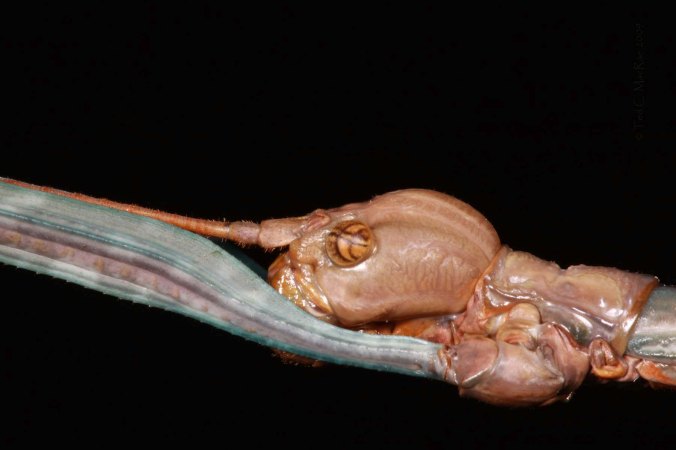 While it may seem that their long, delicate-looking legs are simply “pulled off” by the predator, fortuitously allowing the walkingstick to clamber to safety, leg shed is actually controlled by the central nervous system in response to external stimuli (e.g., grabbing of the leg). Breakage occurs at predetermined abcission points, which are rapidly sealed after shedding to prevent excessive loss of body fluids. I experienced this first hand – lacking any container large enough to hold the enormous female, I gently placed her into my net and gingerly carried her back to the truck, only to find a hind leg already shed by the time I got back. I decided the effort to glue one (or more) legs in place to acheive a well-curated specimen exceeded my interest in starting a collection of this particular group of insects, so I let her go. Presumably she crawled away to safety, though sadly no longer the ‘perfect’ specimen that I first encountered.
While it may seem that their long, delicate-looking legs are simply “pulled off” by the predator, fortuitously allowing the walkingstick to clamber to safety, leg shed is actually controlled by the central nervous system in response to external stimuli (e.g., grabbing of the leg). Breakage occurs at predetermined abcission points, which are rapidly sealed after shedding to prevent excessive loss of body fluids. I experienced this first hand – lacking any container large enough to hold the enormous female, I gently placed her into my net and gingerly carried her back to the truck, only to find a hind leg already shed by the time I got back. I decided the effort to glue one (or more) legs in place to acheive a well-curated specimen exceeded my interest in starting a collection of this particular group of insects, so I let her go. Presumably she crawled away to safety, though sadly no longer the ‘perfect’ specimen that I first encountered.
Photo details:
Photo 1 (full insect): Canon 100mm macro lens on Canon EOS 50D (auto mode), ISO 200, 1/320 sec, f/5.6, natural light.
Photos 2 (midrange) and 3 (closeup): same except (manual mode), ISO 100, 1/60 (Photo 2) or 1/250 (Photo 3) sec, f/10 (Photo 2) or f/20 (Photo 3), MT-24EX flash 1/4 power w/ diffuser caps.
REFERENCES:
Arment, C. 2005. Stick Insects of the Continental United States and Canada: Species and Early Studies. Coachwhip Publications, Landisville, Pennsylvania, 202 pp.
Beamer, R. H. 1932. The giant walking-stick (Megaphasma dentricus (Stal.)) found in Kansas. Journal of the Kansas Entomological Society 5(1):28.
Grimaldi, D. and M. S. Engel. 2005. Evolution of the Insects. Cambridge University Press, New York, xv + 755 pp.
Maginnis, T. L., Cool, C. L. and J. L. Muniz. 2008. Some observations on the mating behavior of the giant walkingstick, Megaphasma dentricus (Orthoptera: Phasmidae). Texas Journal of Science 60(1):57-62.
Copyright © Ted C. MacRae 2009










































































