The term Mountains in Miniature is the most expressive one to describe these bluffs. They have all the irregularity in shape, and in valleys that mountains have, they have no rocks and rarely timber. – Thaddeus Culbertson, missionary, 1852

One of the things I enjoy most about the natural history of Missouri is its diversity. Lying in the middle of the North American continent, it is here where the eastern deciduous forest yields to the western grasslands. Coinciding with this transition between two great biomes is a complex intersection of landforms – the northern plains, recently scoured by glaciers; the southeastern lowlands, where the great Mississippi River embayment reaches its northern extent; the Ozark Highlands, whose craggy old rocks comprise the only major landform elevation between the Appalachian and Rocky Mountains; and the eastern realm of the vast Great Plains. This nexus of east and west, of north and south, of lowlands and highlands, has given rise to a rich diversity of natural communities – 85 in all according to Paul Nelson (2005, Terrestrial Natural Communities of Missouri). Despite the overwhelming changes wrought upon Missouri’s landscape during the past 200 years, passable examples of most of these communities still exist in many parts of the state and provide a glimpse of Missouri’s rich natural heritage.
 Last month I talked about the critically imperiled sand prairie community in extreme southeast Missouri. This month, we travel 500 miles to the distant northwestern corner of the state to visit another critically imperiled community – the dry loess prairie. These communities are confined to thin slivers of bluff top along the Missouri River in Atchison and Holt Counties. The bluffs on which they lie are themselves part of a unique landform called the Loess Hills. Like the sand prairies of the southeastern lowlands, this angular landscape owes its birth to the glacial advances of the Pleistocene epoch (2.5 million to 10,000 years ago), when streams of meltwater – swollen and heavily laden with finely ground sediments (i.e., glacial “flour”) – filled river valleys throughout the Midwest during Pleistocene summers. Brutal cold during winter reduced these flows to a trickle, allowing the prevailing westerly winds to pick up the sediments, left high and dry, and drop them on leeward upland surfaces across Iowa and northern Missouri.
Last month I talked about the critically imperiled sand prairie community in extreme southeast Missouri. This month, we travel 500 miles to the distant northwestern corner of the state to visit another critically imperiled community – the dry loess prairie. These communities are confined to thin slivers of bluff top along the Missouri River in Atchison and Holt Counties. The bluffs on which they lie are themselves part of a unique landform called the Loess Hills. Like the sand prairies of the southeastern lowlands, this angular landscape owes its birth to the glacial advances of the Pleistocene epoch (2.5 million to 10,000 years ago), when streams of meltwater – swollen and heavily laden with finely ground sediments (i.e., glacial “flour”) – filled river valleys throughout the Midwest during Pleistocene summers. Brutal cold during winter reduced these flows to a trickle, allowing the prevailing westerly winds to pick up the sediments, left high and dry, and drop them on leeward upland surfaces across Iowa and northern Missouri.  The thickest deposits occurred along the abrupt eastern border of the Missouri River valley – at least 60 feet deep, and in places up to 200 feet. Loess (pronounced “luss”) is a homogeneous, fine-grained, quartz silt – undisturbed it is highly cohesive and able to stand in near vertical bluffs. It is also extremely prone to erosion, and as a result for 10,000 years now the forces of water have reshaped the Loess Hills into the landform we see today. Loess itself is not rare – thick deposits can be found in many parts of the world and over thousands of square miles across the Midwest. It is here, however, along the western edge of Iowa and northern Missouri – and nowhere else in North America – where loess deposits are deep enough and extensive enough to obliterate any influence by the underlying bedrock and dictate the form of the landscape.
The thickest deposits occurred along the abrupt eastern border of the Missouri River valley – at least 60 feet deep, and in places up to 200 feet. Loess (pronounced “luss”) is a homogeneous, fine-grained, quartz silt – undisturbed it is highly cohesive and able to stand in near vertical bluffs. It is also extremely prone to erosion, and as a result for 10,000 years now the forces of water have reshaped the Loess Hills into the landform we see today. Loess itself is not rare – thick deposits can be found in many parts of the world and over thousands of square miles across the Midwest. It is here, however, along the western edge of Iowa and northern Missouri – and nowhere else in North America – where loess deposits are deep enough and extensive enough to obliterate any influence by the underlying bedrock and dictate the form of the landscape.
It is this form that makes the Loess Hills so unique. The depth of the soil, its cohesiveness, its natural tendency to slump on steep slopes and sheer in vertical planes, and the action of water over the past several millenia have created a landscape of narrow undulating ridges flanked by steep slopes and numerous side spurs,  intricate drainages with sharply cut gullies, and long, narrow terraces called “catsteps” cutting across the steep upper hillsides. It’s a sharp, angular, corrugated landscape, stretching 200 miles north and south in a narrow band of varying width from north of Souix City, Iowa, to its southern terminus in northwestern Missouri. Its western boundary is sharply delimited by the Missouri River valley, where lateral erosion (now halted by channelization of the river) and vertical sheering have created precipitous bluff faces. The eastern boundary is harder to delimit and is dependent upon the thickness of the loess. Deposits that fall below 60 feet in depth are unable to mask and reshape the rolling terrain of the eroded glacial till lying beneath. In general, this happens at distances of only 3 to 10 miles from the western edge of the landform.
intricate drainages with sharply cut gullies, and long, narrow terraces called “catsteps” cutting across the steep upper hillsides. It’s a sharp, angular, corrugated landscape, stretching 200 miles north and south in a narrow band of varying width from north of Souix City, Iowa, to its southern terminus in northwestern Missouri. Its western boundary is sharply delimited by the Missouri River valley, where lateral erosion (now halted by channelization of the river) and vertical sheering have created precipitous bluff faces. The eastern boundary is harder to delimit and is dependent upon the thickness of the loess. Deposits that fall below 60 feet in depth are unable to mask and reshape the rolling terrain of the eroded glacial till lying beneath. In general, this happens at distances of only 3 to 10 miles from the western edge of the landform.
Its southern terminus in Missouri, however, is the most arbitrary boundary. Discontinuous patches of deep loess terrain do occur as far south as Kansas City, but the dry hilltop prairies, common in the north, are gradually replaced by woodland in the south and disappear completely just north of St. Joseph. It is this interdigitation of two great biomes – the great deciduous forest to the east, and the expansive grasslands stretching far to the west – 
 that give the Loess Hills such a fascinating natural history. This is due as much to the physical character of the Loess Hills themselves as to their ecotonal position at the center of the continent. Rapid drainage of rainwater off the steep slopes combines with direct sun and prevailing southwesterly summer winds to create very dry conditions on hilltops and south and west facing slopes, especially on the steeper slopes along the landform’s western edge. Such xeric conditions favor the growth of more drought-tolerant species derived from the western grasslands. North and east facing slopes and valley floors, protected from direct sun and drying winds, are able to retain more moisture, favoring the growth of woody plant species more common in the eastern forests.
that give the Loess Hills such a fascinating natural history. This is due as much to the physical character of the Loess Hills themselves as to their ecotonal position at the center of the continent. Rapid drainage of rainwater off the steep slopes combines with direct sun and prevailing southwesterly summer winds to create very dry conditions on hilltops and south and west facing slopes, especially on the steeper slopes along the landform’s western edge. Such xeric conditions favor the growth of more drought-tolerant species derived from the western grasslands. North and east facing slopes and valley floors, protected from direct sun and drying winds, are able to retain more moisture, favoring the growth of woody plant species more common in the eastern forests.  Seasonal moisture also shows a north-south gradient, with southern latitudes receiving higher annual rainfall totals that also favors the growth of woody plants, while the lower rainfall totals further north result in larger, more expansive grassland habitats. The steep slopes and rapid drainage create much more xeric conditions than those found further south in the flat to rolling terrain of the unglaciated Osage Plain, resulting in a more drought-tolerant mixed-grass prairie rather than the tallgrass prairie of western and southwestern Missouri. The distribution patterns of prairie versus woodland are dynamic and ever-changing, influenced by both natural and anthropogenic processes. Climatic conditions over much of the Loess Hills are capable of supporting either community type, both of which repeatedly expand and shrink as the balance tips in favor of one versus the other.
Seasonal moisture also shows a north-south gradient, with southern latitudes receiving higher annual rainfall totals that also favors the growth of woody plants, while the lower rainfall totals further north result in larger, more expansive grassland habitats. The steep slopes and rapid drainage create much more xeric conditions than those found further south in the flat to rolling terrain of the unglaciated Osage Plain, resulting in a more drought-tolerant mixed-grass prairie rather than the tallgrass prairie of western and southwestern Missouri. The distribution patterns of prairie versus woodland are dynamic and ever-changing, influenced by both natural and anthropogenic processes. Climatic conditions over much of the Loess Hills are capable of supporting either community type, both of which repeatedly expand and shrink as the balance tips in favor of one versus the other.  In the past, the major influence was shifting periods of greater or lesser rainfall. During drier periods, grasslands expanded and woodlands shrank, finding refuge in only the moistest streamside habitats. Wetter periods allowed woody plants to migrate out of the valleys and up the slopes, especially those facing north and east. One particular very dry “hypsithermal” began about 9,000 years ago and lasted for several thousand years. Tallgrass prairies expanded as far east as present day Ohio, and todays tallgrass praires in the eastern Great Plains were invaded by even more drought-tolerant species from the shortgrass prairies further west. Eventually the hypsithermal abated, moisture levels increased, and the grasslands retreated in the face of the advanding forest.
In the past, the major influence was shifting periods of greater or lesser rainfall. During drier periods, grasslands expanded and woodlands shrank, finding refuge in only the moistest streamside habitats. Wetter periods allowed woody plants to migrate out of the valleys and up the slopes, especially those facing north and east. One particular very dry “hypsithermal” began about 9,000 years ago and lasted for several thousand years. Tallgrass prairies expanded as far east as present day Ohio, and todays tallgrass praires in the eastern Great Plains were invaded by even more drought-tolerant species from the shortgrass prairies further west. Eventually the hypsithermal abated, moisture levels increased, and the grasslands retreated in the face of the advanding forest.  Not all of the drought-tolerant species were driven back, however, and scattered populations of these “hypsithermal relicts” still remain on locally dry sites far to the east of their normal range of distribution. Conspicuous examples of such in Missouri’s Loess Hills are soapweed yucca (Yucca glauca var. glauca) and the leafless-appearing skeletonweed (Lygodesmia juncea) (plant above, flower right). Both of these plants are normally found further west in the mixed grass prairies of the western Great Plains but are considered endangered in Missouri due to the great rarity of the dry loess prairies on which their survival depends. (Incidentally, note the crab spider legs extending from behind the petals of the skeletonweed flower). In total, more than a dozen plant species occurring in Missouri’s dry loess prairies are listed as species of conservation concern, along with one reptile (Great Plains skink) and one mammal (Plains pocket mouse).
Not all of the drought-tolerant species were driven back, however, and scattered populations of these “hypsithermal relicts” still remain on locally dry sites far to the east of their normal range of distribution. Conspicuous examples of such in Missouri’s Loess Hills are soapweed yucca (Yucca glauca var. glauca) and the leafless-appearing skeletonweed (Lygodesmia juncea) (plant above, flower right). Both of these plants are normally found further west in the mixed grass prairies of the western Great Plains but are considered endangered in Missouri due to the great rarity of the dry loess prairies on which their survival depends. (Incidentally, note the crab spider legs extending from behind the petals of the skeletonweed flower). In total, more than a dozen plant species occurring in Missouri’s dry loess prairies are listed as species of conservation concern, along with one reptile (Great Plains skink) and one mammal (Plains pocket mouse).
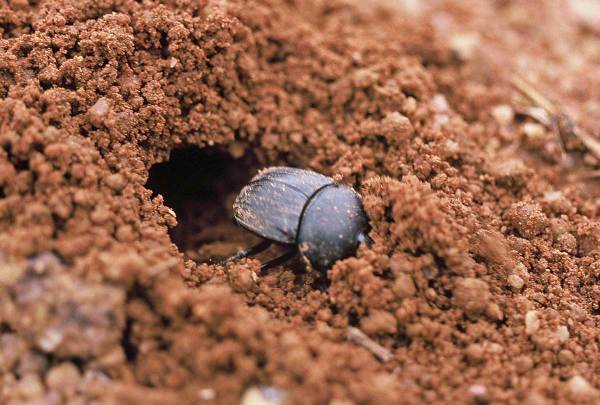
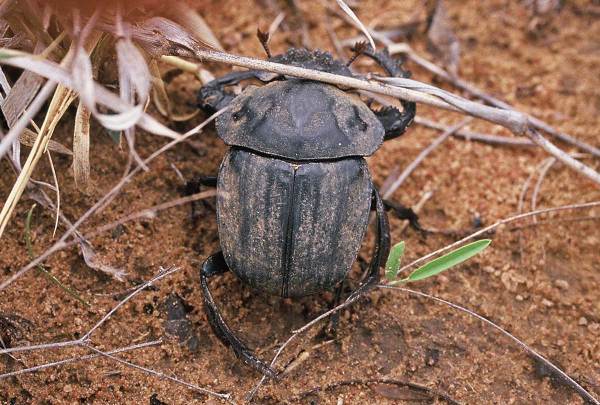
As is typical, the insect fauna of the Loess Hills has been far less studied than its plants, but many of the species that have been documented in its prairies also show affinity to the Great Plains fauna.  Both soapweed and skeletonweed have insect associates that rely exclusively on these hosts for reproduction, and as a result they are also highly restricted in Missouri. Evidence of one of these – a tiny cynipid wasp (Anistrophus pisum) that forms small spherical galls on the stems of skeletonweed – can be seen in the photo above. However, my purpose for visiting the Loess Hills this summer was to look for the rare and possibly endangered tiger beetle, Cicindela celeripes (see this post). Cicindela celeripes has not yet been recorded from Missouri but is known to occur in the Loess Hills of southwestern Iowa, and while I have not succeeded in finding it (yet!) I did observe several adults of this unusual May beetle species, Phyllophaga lanceolata. This May beetle occurs throughout the Great Plains in shortgrass prairie communities.
Both soapweed and skeletonweed have insect associates that rely exclusively on these hosts for reproduction, and as a result they are also highly restricted in Missouri. Evidence of one of these – a tiny cynipid wasp (Anistrophus pisum) that forms small spherical galls on the stems of skeletonweed – can be seen in the photo above. However, my purpose for visiting the Loess Hills this summer was to look for the rare and possibly endangered tiger beetle, Cicindela celeripes (see this post). Cicindela celeripes has not yet been recorded from Missouri but is known to occur in the Loess Hills of southwestern Iowa, and while I have not succeeded in finding it (yet!) I did observe several adults of this unusual May beetle species, Phyllophaga lanceolata. This May beetle occurs throughout the Great Plains in shortgrass prairie communities.  Larvae feed in the soil on roots of grasses and other plants, while adults feed above ground on flowers and foliage. The heavy-bodied adults are unusual in the genus due to their conspicuous covering of scales (most species of Phyllophaga are glabrous or with sparsely scattered and indistinct setae) and by being active during the day. They are also relatively poorer fliers and are thus usually observed moving about on foot – as seen with this individual who was found on bare soil below a vertical cut. This snakeweed grasshopper (Hesperotettix viridis, ID by Eric R. Eaton) is another species more typically seen in the western United States, although populations have been found from across the continent. Preferred host plants include a variety of asteraceous shrubs, but as suggested by the common name snakeweeds (Xanthocephalum spp.) are highly preferred and account for its greater abundance in the west. Populations in northern and eastern portions of its range,
Larvae feed in the soil on roots of grasses and other plants, while adults feed above ground on flowers and foliage. The heavy-bodied adults are unusual in the genus due to their conspicuous covering of scales (most species of Phyllophaga are glabrous or with sparsely scattered and indistinct setae) and by being active during the day. They are also relatively poorer fliers and are thus usually observed moving about on foot – as seen with this individual who was found on bare soil below a vertical cut. This snakeweed grasshopper (Hesperotettix viridis, ID by Eric R. Eaton) is another species more typically seen in the western United States, although populations have been found from across the continent. Preferred host plants include a variety of asteraceous shrubs, but as suggested by the common name snakeweeds (Xanthocephalum spp.) are highly preferred and account for its greater abundance in the west. Populations in northern and eastern portions of its range,  which would include northern Missouri, are considered subspecies pratensis, while the more southern and western populations are considered the nominotypical subspecies. Interestingly (and unlike many grasshoppers), this species is considered beneficial by ranchers, since the plants on which it prefers to feed are either poisonous to livestock or offer little nutritional value while competing with more desirable forage plants for soil moisture. While exploring the upper slopes, I encountered sporadic plants of two of Missouri’s more interesting species of milkweed – whorled milkweed (Asclepias verticillata) and green milkweed (Asclepias viridiflora), raising my hopes that I might encounter one of the many Great Plains species of milkweed beetles (genus Tetraopes). However, the only species I observed was the common milkweed beetle, Tetraopes tetrophthalmus, which occurs broadly across eastern North America on the equally broadly distributed common milkweed (Asclepias syriaca).
which would include northern Missouri, are considered subspecies pratensis, while the more southern and western populations are considered the nominotypical subspecies. Interestingly (and unlike many grasshoppers), this species is considered beneficial by ranchers, since the plants on which it prefers to feed are either poisonous to livestock or offer little nutritional value while competing with more desirable forage plants for soil moisture. While exploring the upper slopes, I encountered sporadic plants of two of Missouri’s more interesting species of milkweed – whorled milkweed (Asclepias verticillata) and green milkweed (Asclepias viridiflora), raising my hopes that I might encounter one of the many Great Plains species of milkweed beetles (genus Tetraopes). However, the only species I observed was the common milkweed beetle, Tetraopes tetrophthalmus, which occurs broadly across eastern North America on the equally broadly distributed common milkweed (Asclepias syriaca).
It is a familiar refrain, but Missouri’s dry loess hill prairie communities are critically endangered. Historically, these communities were probably never as well developed as those further north, and only a few small remnants remain today due to significant woody encroachment following decades of fire suppression. Much of this encroachment has occurred in the past 50 years – Heinman (Woody Plant Invasion of the Loess Hill Bluff Prairies. M. A. Thesis, University of Nebraska at Omaha, 1982) used aerial photographs to show a 66 percent encroachment of shrubs and trees into the loess hill mixed-grass prairies between 1940 and 1981. Additional threats include overgrazing, erosion, invasion by exotic plant species and homesite development. Fewer than 50 acres of native dry loess hill prairie remain in Missouri – only half of which are now in conservation ownership. The majority of these can be found at Star School Hill Praire and Brickyard Hill Conservation Areas in Atchison County and at McCormack Conservation Area just to the south in Holt County. Controlled burning and selective cutting are being used at these sites to control woody plant invasions, but even these management techniques present challenges. Spring burns have been shown to promote the growth of big bluestem (Andropogon gerardii), which could allow it to encroach drier areas where mid-grasses such as little bluestem (Schizachyrium scoparium) and sideoats grama (Bouteloua curtipendula) typically dominate (Rushin 2005). Increases in tall grasses could shade out and eliminate some of the rarer low-growing forbs such as downy painted cup (Castilleja sessiliflora), locoweed (Oxytropis lambertii) and low milkvetch (Astragalus lotiflorus). Fall or winter burns may be more beneficial to forbs because the plants are allowed to complete flowering and seed set, but the steep slopes on which these communities occur make erosion a potential concern. Clearly, all factors must be considered when designing management plans for this rare and significant slice of Missouri’s natural heritage.

In addition to the links and references provided above, I highly recommend Fragile Giants: A Natural History of the Loess Hills, by Cornelia F. Mutel (1989). All of the above photographs were taken at Star School Hill Prairie Conservation Area on July 12, 2008. Additional photographs of Loess Hill habitats in extreme southwestern Iowa appeared in my earlier post, The hunt for Cicindela celeripes. The plants shown in photographs 5-7 are purple praire clover (Dalea purpurea), white prairie clover (D. candida), and lead plant (Amorpha canescens), respectively. Lastly, I would like to apologize for the length of this post – a consequence of my inability to temper my utter fascination with the natural world and desire to understand the depths its connectedness.