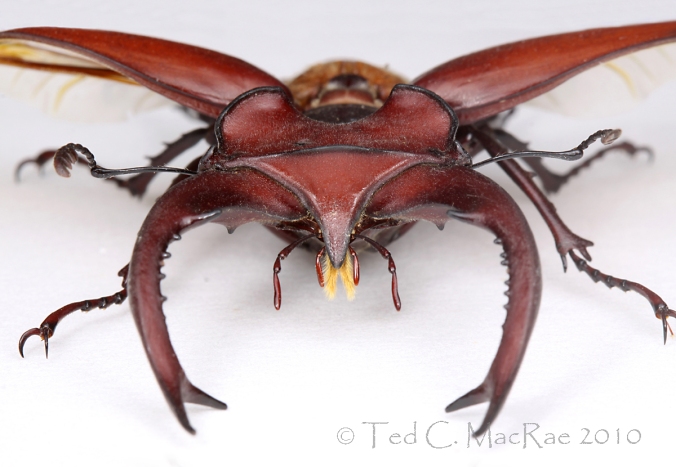
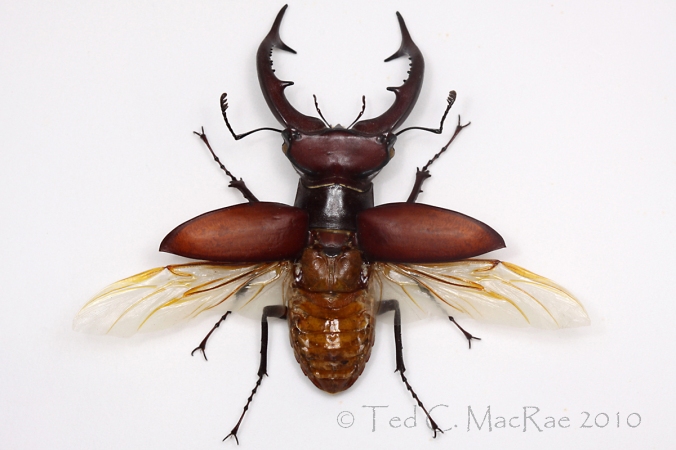
Here is the full-sized photo that provided the image for yesterday’s Super Crop Challenge #3. The insect in the photo is, of course, a fine example of a male Lucanus elaphus – the giant stag beetle (family Lucanidae). This striking insect is easily among North America’s most distinctive and recognizable species by virtue of the enormously super-sized mandibles sported by the males. Its fearsome appearance belies the true nature of this harmless beetle, which spends its days feeding on sap that flows from wounds on the trunks and roots of trees. Males use their massive mandibles in combat with other males, not for “biting,” but rather as tools to pry and lift their adversaries before dropping them to the ground. Some marvelous photos of this behavior in a related European species can be seen at Stag Beetles Lucanus cervus Mating Behaviour.
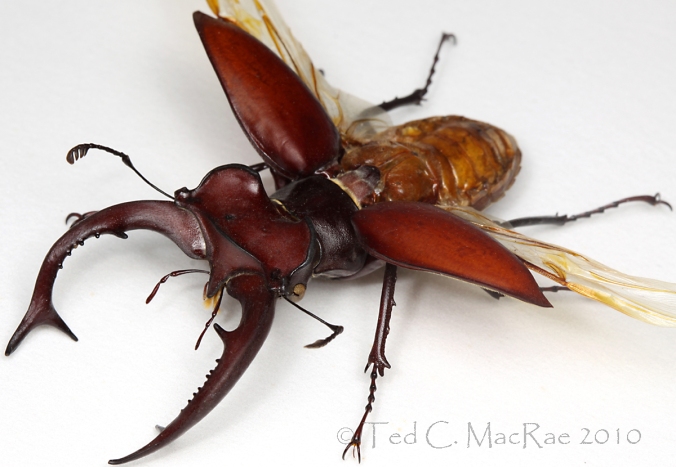

I collected this specimen many years ago at an ultraviolet light (“blacklight”) that I had setup in the pine/oak forests at Pinewoods Lake, Carter Co., in the southeastern Ozarks – one of my favorite 1980’s beetle collecting spots. This was in my early days of studying beetles, during which time I was actively collecting material as part of my statewide surveys for the families Buprestidae (MacRae 1991) and Cerambycidae (MacRae 1994). Lucanus elaphus is not a commonly encountered species, especially in the western reaches of its distribution here in Missouri, and I’ll never forget my rabid excitement when I encountered this fine major male at my blacklight sheet. For many years afterward it remained the only individual that I had ever encountered, until a few years ago when I came across a group of two males and one female feeding on a sap flow in a wet bottomland forest along the Mississippi River in the lowlands of southeastern Missouri. I encountered another male the following year at a nearby location “rafting” on debris in floodwaters from the nearby river, and two weeks later at that same site I picked up several males and females in a fermenting bait trap.¹ Like most “uncommon” species with broad distribution across the eastern U.S., I suspect that its apparent rarity is an artifact due to habits that make it infrequently encountered rather than being truely scarce.
¹ I have used fermenting bait traps to collect a wide variety of beetles, but especially longhorned beetles. My recipe is based on that described by Champlain and Knull (1932) – bring 12 oz. dark molasses and 12 oz. beer up to 1 gal. with water, mix well and add a packet of dry baker’s yeast to get the fermentation started. Hang a 1/2-gallon milk jug with big holes cut in the sides in a tree along the edge of a woods and add ~1 quart of fresh liquid. It generally takes 2-3 days for the liquid to really start fermenting and become attractive, and it will remain so for about another week or so. Check traps every 2-3 days by pouring the liquid through a kitchen strainer into another container – reuse or replace as necesssary. Place the collected specimens in vials of water to wash off the molasses residues, and either pin immediately afterward or transfer to 70% ethanol for longer term storage. Some of the more desireable species I’ve collected in this manner, besides L. elaphus, are Plinthocoelium suaveolens, Purpuricenus axillaris, P. humeralis, P. paraxillaris, Stenocorus cylindricollis, S. shaumii, Sarosesthes fulminans, Stenelytrana emarginata [= Leptura emarginata], and S. gigas [= Leptura gigas].

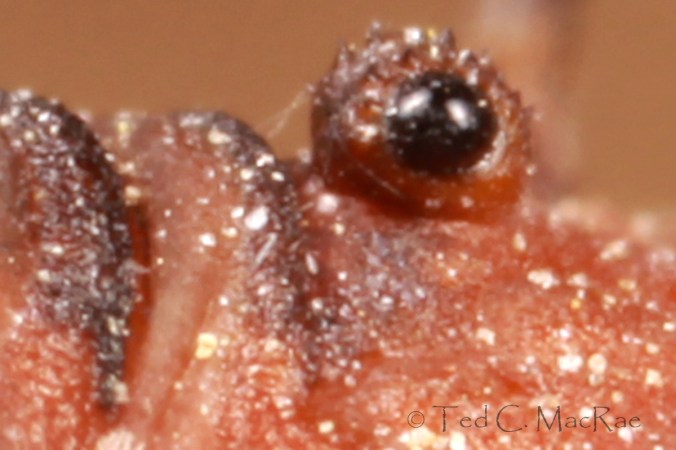
Congratulations to Ben Coulter and Janet Creamer, both of whom correctly identified the species and most of the mouthparts. Each earned 14 pts and, thus, tied for the win, while JasonC. earned 5 pts. to take the final podium spot. The pointed structure is the labrum (its shape distinguishing it from other North American species of the genus), and it is flanked on each side by the fuzzy yellow galeae (derived from the maxillae) and the labial palps. Nobody correctly named the galeae, which seem to be greatly elongated and hairy in stag beetles as a function of their sap feeding behavior. A portion of the left maxillary palpus can also be seen in the corner of the photograph, but nobody scored those points either. Brady Richards just missed the podium, but his witty reference to Gene Shalit (if not immediately picked up on by me) earns him an honorable mention.
With points being formally awarded now beginning with the previous competition (ID Challenge #1), I’ll start keeping an overall leaders board, and with wins in both competitions Ben takes a commanding lead in the overalls with 23 pts, followed by Janet Creamer at 14 pts and TGIQ at 8 pts. I guess I should start thinking of some sort of tangible prize for winners periodically – suggestions welcome. Stay tuned for another issue of Super Crop Challenge or ID Challenge in the near future.
REFERENCES:
Champlain, A. B. and J. N. Knull. 1932. Fermenting bait traps for trapping Elateridae and Cerambycidae (Coleop.). Entomological News 43(10):253–257.
MacRae, T. C. 1991. The Buprestidae (Coleoptera) of Missouri. Insecta Mundi 5(2):101–126.
MacRae, T. C. 1994. Annotated checklist of the longhorned beetles (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae and Disteniidae) known to occur in Missouri. Insecta Mundi 7(4) (1993):223–252.
Copyright © Ted C. MacRae 2010